CIE A Level Biology复习笔记14.2.2 Guard Cells翰林国际教育
Structure of Guard Cells. Guard cells are a pair of bean or kidney-shaped cells which surround the stomata. These specialized cells are found on the plant epidermis, or outer layer of the plant..

Plant Guard Cells With Stoma Fully Labeled. Stock Image 51409771
Functions Guard Cells in Plants Definition In plants, guard cells refer to the protective layer around a stoma that facilitates gas exchange between the plant cells and surrounding. Several pores are found in the leaves, and the cross-sectional view of the leaf cells to let us know the location of guard cells.
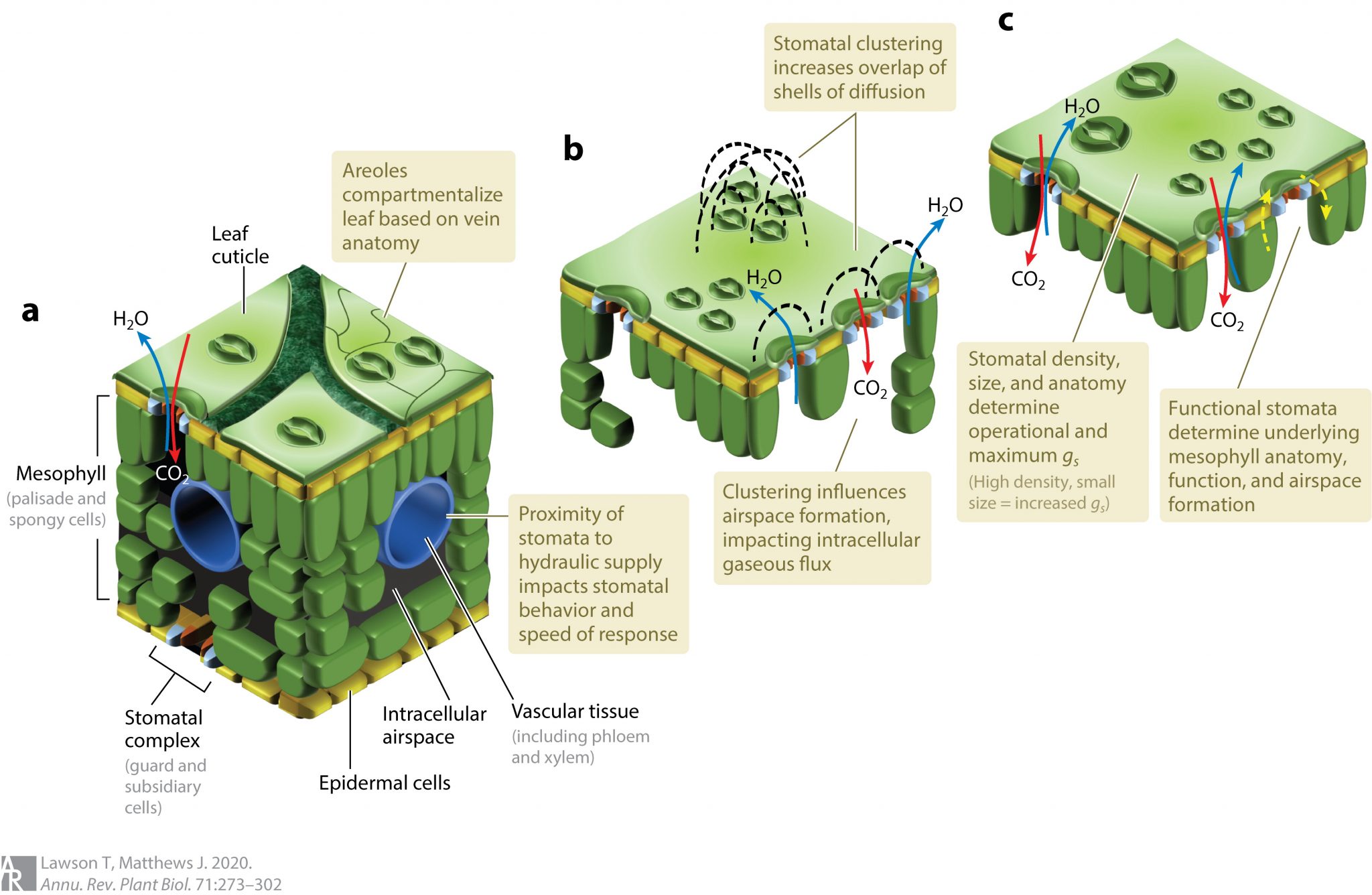
Plantae Review Guard cell metabolism and stomatal function (Annu. Rev. Plant Biol.) Plantae
Guard Cells Diagram Structure They are bean or kidney-shaped cells found on the epidermis of a plant. Between two guard cells is a pore called a stoma that regulates gas exchange in plants. Each guard cell has a thick cuticle on the pore-side and a thin-one on the opposite side.
What are guard cells? Explain their role in regulating transpiration
Guard cells are key regulators of salinity tolerance in plants. When thinking about the role of stomata in protection against salinity damage, it is intuitively expected that stomatal closure reduces transpiration as well accumulation of toxic ions in the plant canopy.

how to draw surface view and lateral view view of guard cell and epidermal cell YouTube
Guard cells are cells surrounding each stoma. They help to regulate the rate of transpiration by opening and closing the stomata. Light is the main trigger for the opening or closing. Each guard cell has a relatively thick and thinner cuticle on the pore-side and a thin one opposite it.

B2 V) Stomata & Guard Cells AQA Combined Science Trilogy Elevise
GCSE Edexcel Plant organisation - Edexcel Transport and structure of specialised plant cells Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis and gas exchange. Roots absorb water and mineral ions.

Difference Between Guard Cells and Subsidiary Cells Compare the Difference Between Similar Terms
Guard cells are pairs of epidermal cells that control gas diffusion by regulating the opening and closure of stomatal pores. Guard cells, like other types of plant cells, are surrounded by a three-dimensional, extracellular network of polysaccharide-based wall polymers. In contrast to the walls of diffusely growing cells, guard cell walls have been hypothesized to be uniquely strong and.

Guard Cells Plants
Explore about the diagram, types and guard cells." Table of Content ; Any of the minute openings or pores in the epidermis of leaves and young stems, often termed stomate, stoma, plural stomata, or stomas. On the underside of leaves, stomata are found extensively. They allow gases to flow between the leaf's branching system of interconnecting.

Guard Cells Definition, Location, Structure, Function and Diagram of Guard Cells CBSE Class
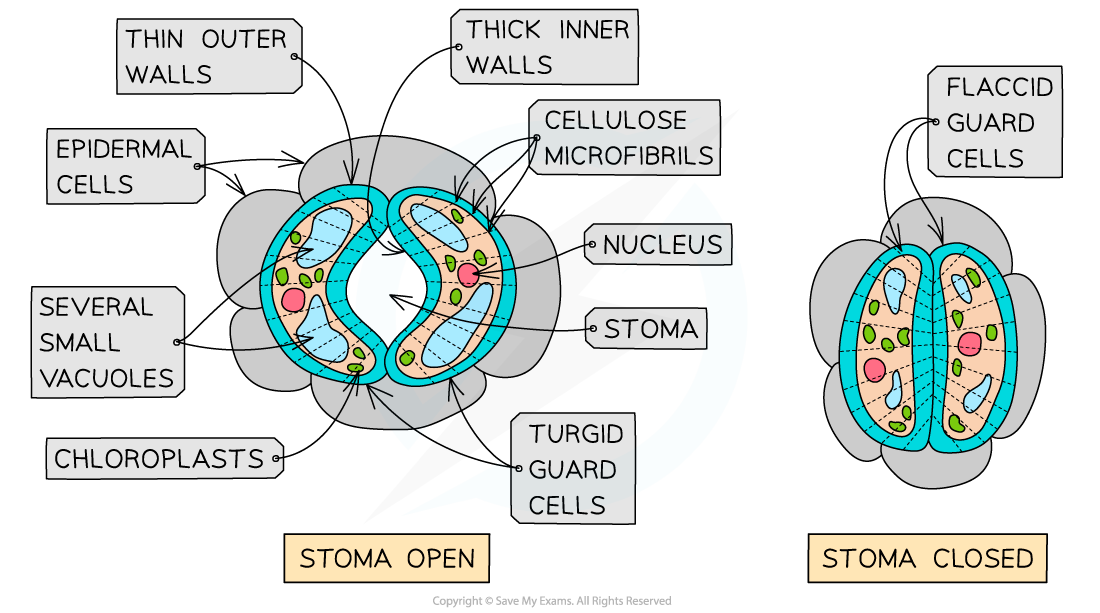
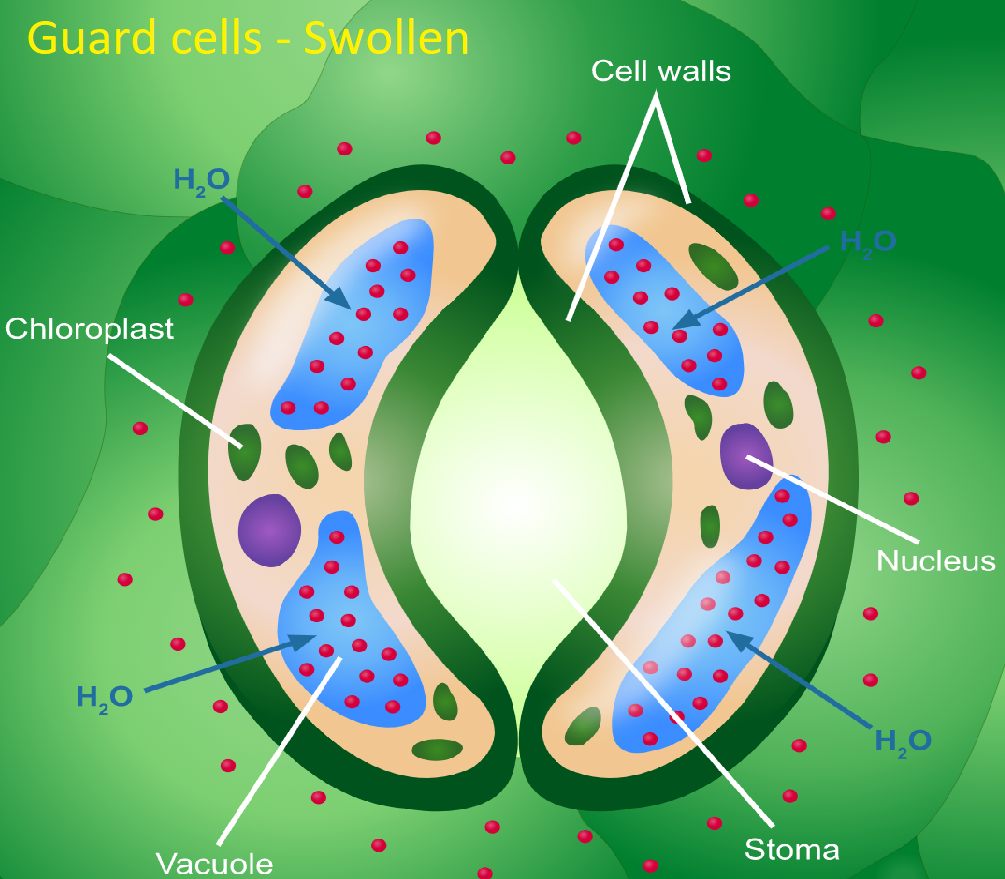
Test Yourself Guard Cells Structure of guard cells Each stoma is surrounded by two guard cells Guard cells have the following features: Thick cell walls facing the air outside the leaf and the stoma Thin cell walls facing adjacent epidermal cells Cellulose microfibrils arranged in bands around the cell Cell walls have no plasmodesmata

Diagram showing stomata and guard cell Royalty Free Vector
*guard cell* Either of a pair of cells that control opening and closing of a leaf pore (stoma [1]). Each is a sausage- or kidney-shaped cell whose wall varies in rigidity. The wall bordering the pore is thickened and rigid, whereas the outside wall is thin and extensible.

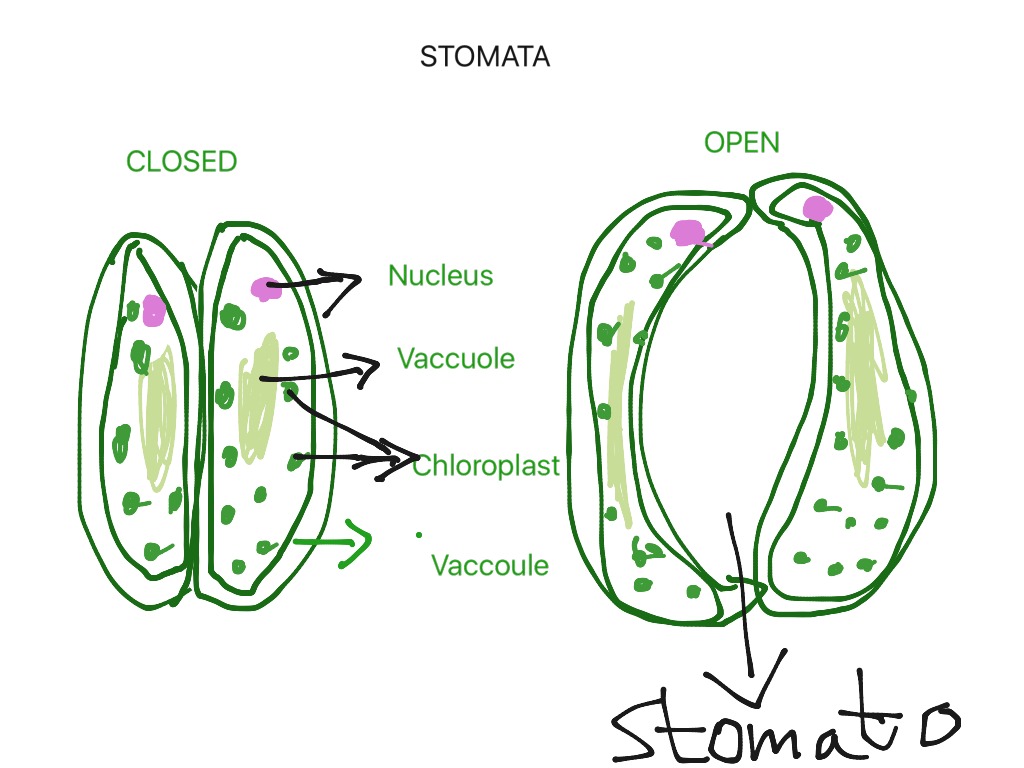
Draw a labeled diagram of stomata when guard cells are turgid.
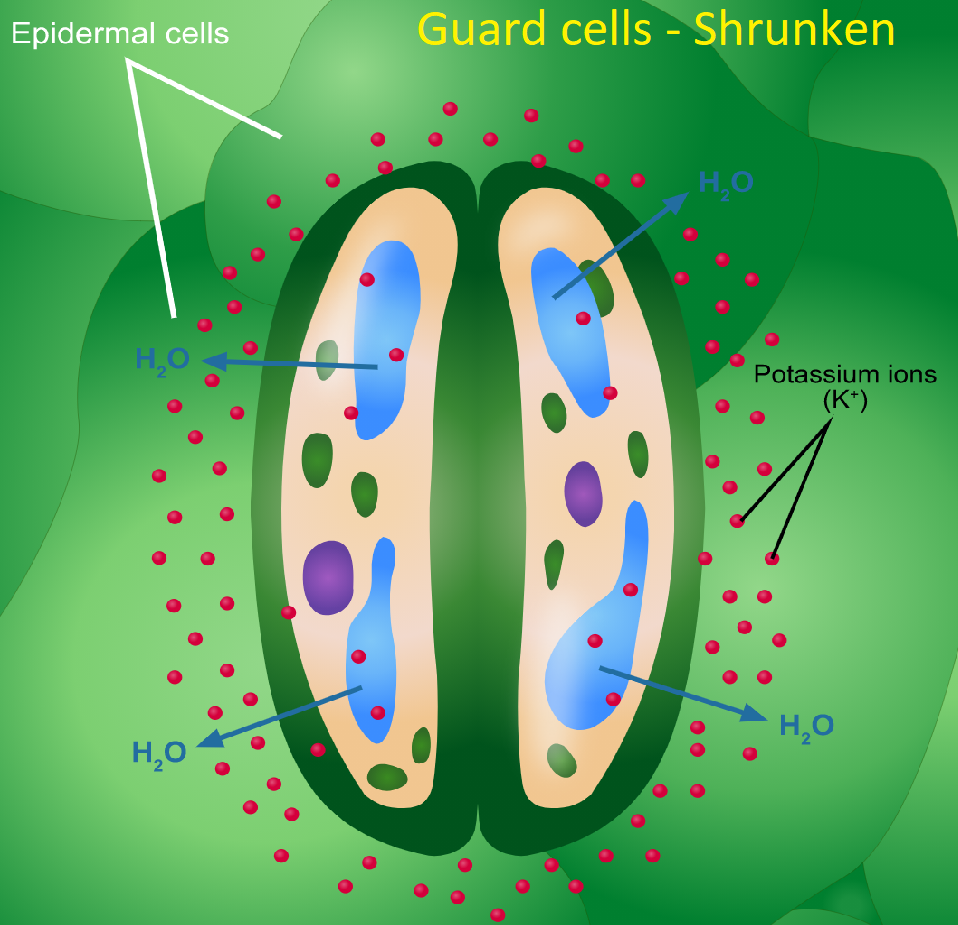
One way to track dynamic changes in guard cell vacuoles during stomatal movements is to use cell imaging techniques, such as confocal microscopy and TEM. In 2005, Gao et al. did just this when.
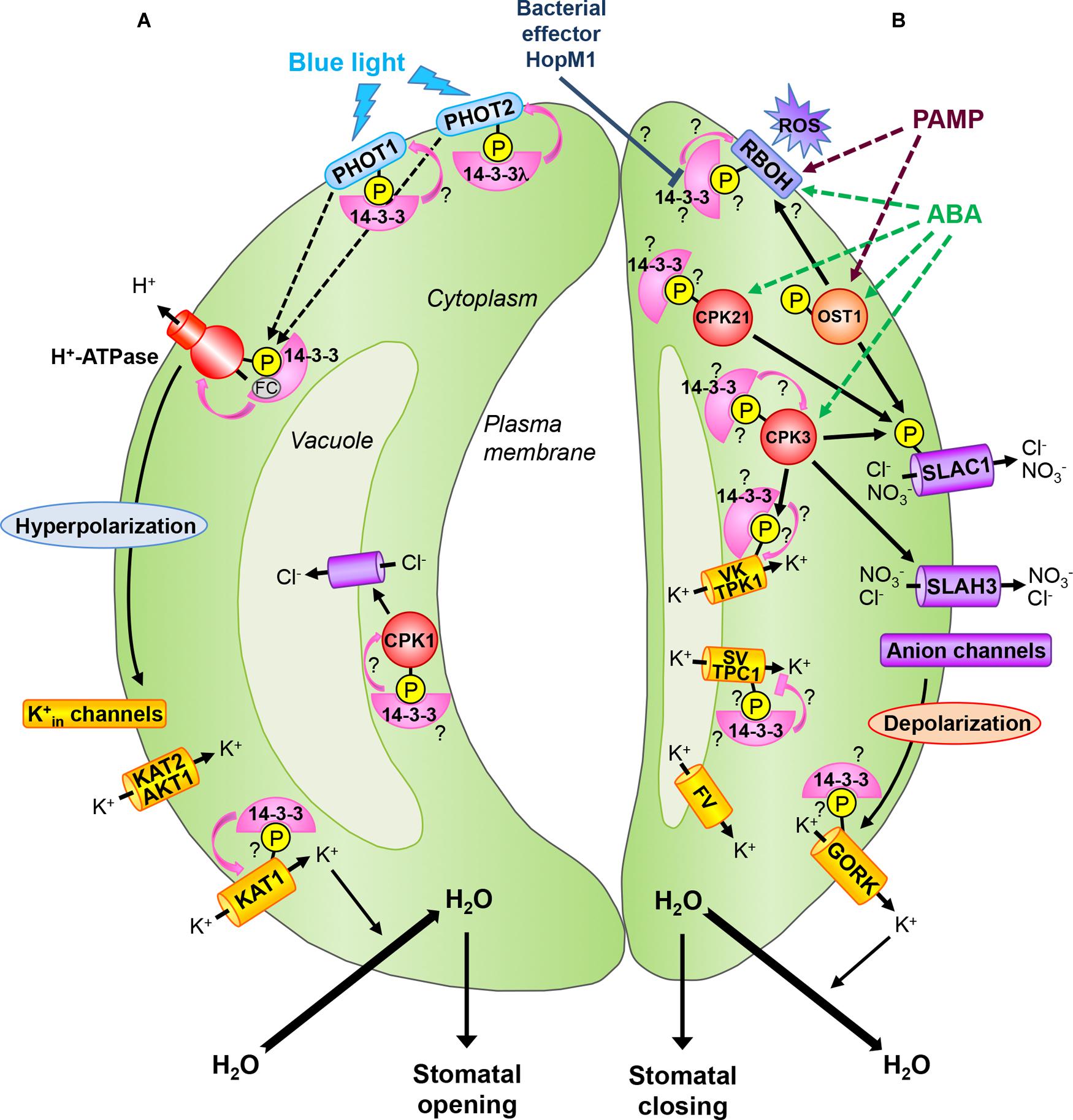
Frontiers 1433 Proteins in Guard Cell Signaling Plant Science
Guard cells are defined in biology as a pair of crescent-shaped cells that surround a pore (stoma) in the epidermis. The stoma opens and closes due to changes in the turgidity of the cells. Guard cell functions The main function of guard cells in a leaf is in their ability to become turgid and flaccid.
What are guard cells? Explain their role in regulating transpiration
Figure 4.5.1.2.2.1 4.5.1.2.2. 1: Italian chicory leaf epidermis showing stomata. The epidermal cells are shaped like puzzle pieces. The stomata (singular = stoma) are pores in the epidermis. Each is bordered by two guard cells, which are filled with oval, green chloroplasts. Image by Umberto Salvagnin ( CC-BY ).

Describe the walls of guard cells.
guard cell plant anatomy Learn about this topic in these articles: angiosperms In angiosperm: Dermal tissue.the epidermis are paired, chloroplast-containing guard cells, and between each pair is formed a small opening, or pore, called a stoma (plural: stomata).

what are the function of guard cells? Brainly.in
Definition, Function, Structure of Stomata on Plants Definition: What is a Guard Cell? Essentially, guard cells are two bean-shaped cells that surround a stoma. As epidermal cells, they play an important role in gaseous exchange in and out of plant leaves by regulating the opening and closing of pores known as a stoma.
STRUCTURE OF GUARD CELLS (stomata) Science, Biology, Plants ShowMe
Stomata. Stomata (singular stoma) are tiny openings or pores found in the epidermis of leaves and young stems that helps in gas exchange. Pair of specialized bean-shaped cells called guard cells are found to surround each stoma. Just like animals breathe, plants do so with the help of stomata.